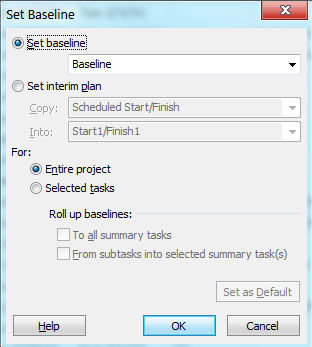
When you create baseline it stores all the information about tasks in five categories: start dates, finish dates, durations, work, and cost estimates) sometime you want only to track dates for comparisons you can use Interim plans. An interim plan is a set of current project data that you save after the project begins and that you can compare against the baseline to assess project progress. An interim plan saves only two kinds of information: the current start dates and finish dates for tasks. Remember you can set up to 10 interim plans for a project so don't afraid of using same.
After setting up an Interim Plan in MS Project, the next steps typically involve tracking and analyzing the project's progress against the established baseline.
Once you setup your Interim Plans, you can now follow below steps
Update Actual Progress: As work on your project progresses, regularly update the actual progress of tasks in MS Project. This includes updating task durations, marking tasks as complete, and entering actual start and finish dates.
Compare Baseline and Actual: MS Project provides various views and reports that allow you to compare the Interim Plan (baseline) with the current project schedule (actual). These comparisons help you identify any deviations, delays, or changes in the project.
Analyze Variances: Review the variances between the baseline and actual data to identify areas where the project is deviating from the original plan. MS Project offers features like the "Tracking Gantt" view and "Variance" table that can assist in analyzing these differences.
Adjustments and Rescheduling: Based on the variances you observe, you may need to make adjustments to your project schedule. You can update task durations, add or remove tasks, adjust dependencies, or allocate additional resources as necessary to realign the project with its objectives.
Communicate Updates: Share progress updates and reports with stakeholders and project team members. This helps keep everyone informed about the project's status and any changes that have occurred.
Monitor and Track Changes: Continuously monitor the project's progress and update the Interim Plan accordingly. Capture new Interim Plans at significant milestones or when substantial changes occur to maintain an accurate historical record.
Perform Trend Analysis: Over time, use the Interim Plans and historical data to analyze trends and patterns in the project's performance. This analysis can help identify recurring issues, assess the effectiveness of corrective actions, and improve future project planning.
Iterative Process: Project management is an iterative process, so you'll repeat these steps throughout the project's lifecycle. Set new baselines as needed, track progress, analyze variances, and make adjustments to ensure the project stays on track.
By following these steps, you can effectively monitor, track, and adjust your project's progress based on the Interim Plan you have set up in MS Project. It helps you stay informed, make data-driven decisions, and keep your project on course towards successful completion.